The Function & Operation of Rubber Bladder Valves
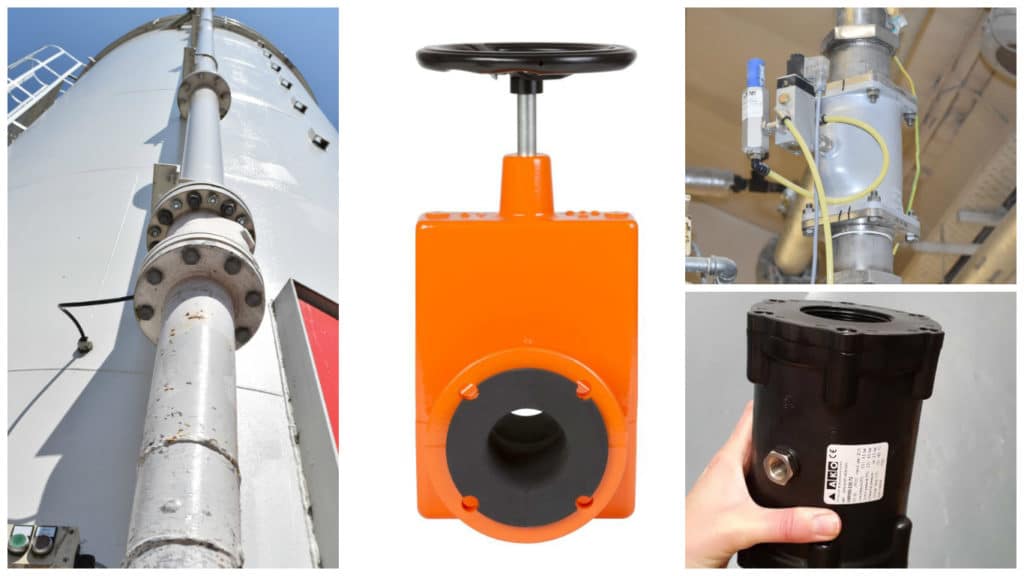
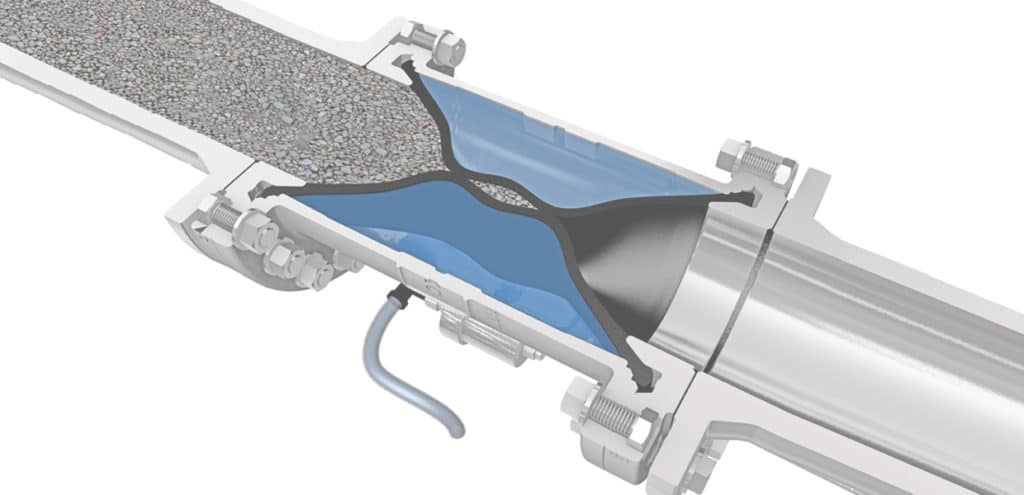
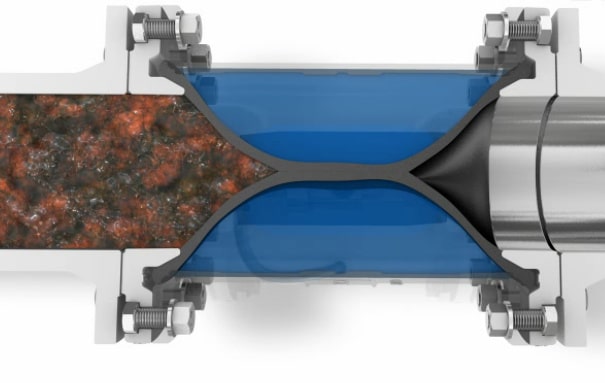
Rubber bladder valves are mainly used as a shut off valve for any bulk and solids, suspensions, sludge’s or fibrous and corrosive media, and they are also used as throttle or dosing valves. When using the bladder valve as a throttle valve it needs the control from an electro proportional pressure control valve. Otherwise if it is used as a shut off valve, normally the control takes place through a 3/2-way solenoid valve.